Did you know? Over 30% of adults age 40 and up experience measurable declines in testosterone levels — but with the right diet, you can help boost your body’s hormone production naturally and feel the difference in your energy, strength, and mood.
If you care about muscle strength, sharper focus, or simply want to feel more vital, understanding how diet for testosterone production works is crucial. Whether you’re a man or woman, your testosterone level plays a foundational role in performance, motivation, and long-term well-being. This guide reveals what foods and nutrients boost testosterone, what lowers it, and how to structure your meals for optimal hormone balance — all based on research and the latest expert insights.
The Critical Role of Diet for Testosterone Production
"Testosterone is foundational for both men and women — it shapes strength, mood, motivation, and overall vitality."
When most people hear “testosterone,” they picture it as a men’s hormone. In reality, both men and women rely on healthy testosterone levels for everything from muscle strength and metabolism to steady energy, focus, and emotional resilience. As we age, testosterone levels tend to decline — but diet is a proven tool to slow that slide and even boost testosterone naturally. Multiple studies demonstrate that certain foods help increase testosterone production, while excess processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can quickly lower testosterone, negatively impacting hormone levels and overall health.
If you want to avoid the pitfalls of low testosterone — like reduced muscle mass, low motivation, or mood swings — it’s time to see food as your first line of support. Focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods lays the groundwork for healthy testosterone and long-term vitality, no matter your age or gender. In the following sections, you’ll discover what to eat, what to avoid, and science-backed techniques to fuel healthy hormone production every day.

What You'll Learn About Diet for Testosterone Production
- How diet for testosterone production influences health in men and women
- Foods and nutrients that boost testosterone
- What lowers testosterone and how to avoid it
- Practical meal plans and food tips
- Expert insights and research on diet for testosterone production
The Science: How Diet Affects Testosterone Levels
Understanding the connection between diet for testosterone production and hormone health starts with the basics. Testosterone, a critical sex hormone in both men and women, is made from cholesterol. This means the types of fats and nutrients you eat directly affect testosterone levels and overall hormone production. Clinical data show that men with diets high in processed foods tend to have lower testosterone, while diets rich in fatty fish, healthy fats, and micronutrients help boost testosterone and support healthy metabolism, energetic mood, and muscle recovery. Even among healthy adults, shifting your nutrition can result in noticeable improvements in how you feel, look, and function day to day.
Low testosterone isn’t just about low sex drive — in both men and women, it can cause fatigue, unstable mood, brain fog, and even bone loss. The right food plan is fundamental for anyone seeking higher testosterone levels, better vitality, and a stronger body. The science is clear: food choices can directly raise or reduce your serum testosterone and set the stage for robust energy and wellness at every age.
Understanding Testosterone Deficiency: Key Symptoms in Men & Women
- Fatigue
- Reduced muscle strength
- Mood changes
- Low libido
- Bone loss
Testosterone deficiency often flies under the radar, especially in women, but its impact is far-reaching. Many people don’t realize that the symptoms they attribute to aging or everyday stress — like feeling tired all the time or struggling with muscle strength — can be tied to low testosterone. This deficiency affects both men and women, though it tends to manifest differently depending on sex and age. In men, low testosterone may show up as drops in muscle mass, problems with libido or sex drive, and slower recovery from workouts. Women may notice changes in mood, lower motivation, and even more pronounced bone loss after menopause — a period marked by a sharp decrease in hormone production, including testosterone. If you’ve experienced persistent symptoms like these, making changes to your diet could be a vital first step in restoring healthy hormone levels and regaining your zest for life.

How Diet Supports Testosterone Production and Balance
Your daily diet can either provide the building blocks for robust testosterone production or undermine it. Essential nutrients like omega-3s, zinc, and magnesium act as co-factors in the intricate process your body uses to synthesize testosterone. For instance, fatty fish like salmon and sardines are loaded with healthy fats and cholesterol, helping maintain the raw materials needed for hormone production. On the flip side, excessive processed foods or added sugar can reduce testosterone and disrupt the delicate balance your body strives for. Emerging research suggests that even moderate changes in food quality can lead to significant changes in serum testosterone levels within a few weeks.
It’s not just about what you eat, but also when and how consistently. A balanced diet that emphasizes whole foods, lean proteins, and micronutrient-rich plants can affect testosterone positively, helping both men and women retain vitality, muscle strength, and healthy metabolic function. Habits such as regular resistance training and minimizing stress further enhance these dietary benefits, creating a synergistic effect for stronger and more stable hormone levels.
Startling Facts: Diet’s Impact on Testosterone Production
- Over 30% of adults over 40 have measurable declines in testosterone levels.
- Processed foods and excess sugar linked with lower testosterone in clinical studies.
- Diets rich in healthy fats and whole foods correlate with higher testosterone levels.
One of the most convincing arguments for focusing on diet for testosterone production is the weight of the current evidence. Studies consistently reveal that individuals whose diets are high in processed snacks, sugary drinks, and trans fats are far more likely to experience low testosterone, sluggishness, and poor muscle strength. Meanwhile, people who eat more whole foods, embrace healthy fats like those found in avocados and nuts, and consume plenty of leafy greens and lean proteins tend to enjoy higher testosterone levels and a lower risk of metabolic decline. Your nutrition choices today don’t just set you up for better hormone health tomorrow — they play a role in how energized, resilient, and motivated you feel every single day.
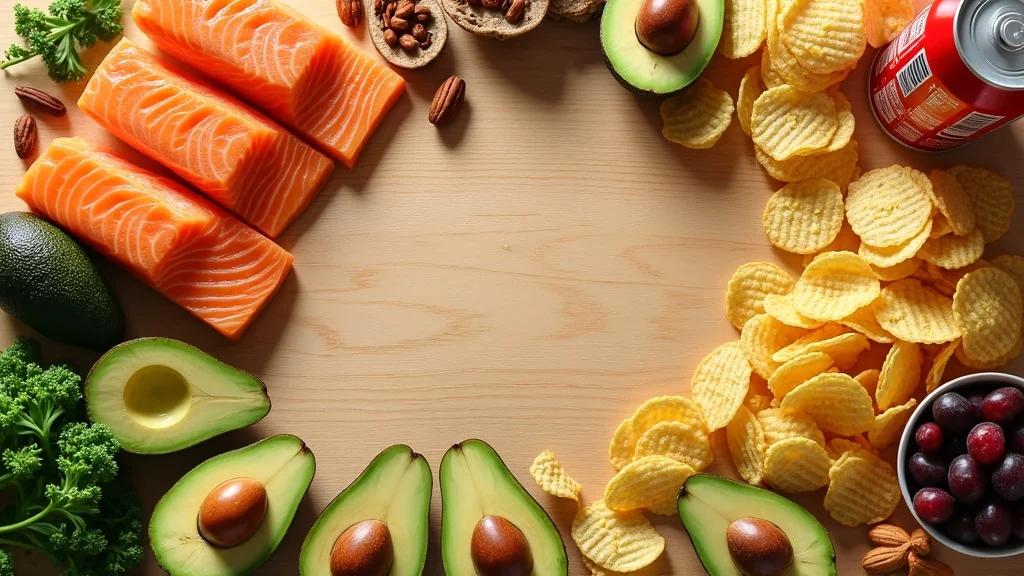

Boost Testosterone: The Core Nutrients in a Diet for Testosterone Production
If you want to increase testosterone naturally, focus on three groups of nutrients: healthy fats from fatty fish, vital minerals like zinc and magnesium, and high-quality protein. Each has a unique effect on testosterone production and overall health. Ignoring any group can lead to suboptimal results, affecting your testosterone level, metabolic health, and even your mental sharpness.
Balancing your meals to include these foods supports not only robust hormone production but also can assist in maintaining healthy weight, supporting muscle mass, and keeping you more energetic throughout the day. Let’s dive into what makes each nutrient group so essential—and the best foods to add to your shopping cart.
Healthy Fats and Fatty Fish: Essential for Testosterone Levels
- Omega-3s and Omega-6s — found in salmon, mackerel, sardines
- Cholesterol — a fundamental building block for testosterone production
Healthy fats — especially those from fatty fish — are crucial in any diet for testosterone production. Cholesterol, often unfairly maligned, is the raw material your body turns into testosterone. Omega-3 fatty acids, abundant in salmon, mackerel, and sardines, help reduce inflammation and create the ideal internal environment for hormone synthesis. Eating these foods preserves healthy cell membranes and helps regulate hormone levels. For healthy men, including two servings of fatty fish each week has been shown to promote optimal testosterone levels and improve metabolic markers linked to muscle strength and healthy body fat.
Plant-based sources like avocado, olive oil, and nuts also support healthy testosterone, though the omega content differs. What matters most is the type and balance of fats: focus on whole food sources and steer clear of trans fats or highly processed seed oils that can lower testosterone and harm long-term wellness.

Zinc, Magnesium, and Vitamin D: Key Micronutrients for Testosterone Levels
- Shellfish (oysters, crab)
- Pumpkin seeds, nuts
- Egg yolks, fortified milk
Zinc, magnesium, and vitamin D are powerful drivers of hormonal health and are proven to boost testosterone when incorporated regularly into your diet. Zinc, found abundantly in oysters and shellfish, supports hormone production and enhances immune defense. Even modest zinc deficiency has been linked to lower testosterone level and waning sex drive in men and women. Magnesium, present in seeds, leafy greens, and nuts, helps optimize muscle strength and stress responses, key factors in stable testosterone. Meanwhile, vitamin D, best absorbed from sunlight but also found in egg yolks and fortified milk, is closely tied to serum testosterone levels — studies confirm that vitamin D supplementation in deficient individuals raises both total and free testosterone.
Combining these micronutrients through whole food sources and smart supplementation creates the best circumstances for your body’s own testosterone production, guarding against testosterone deficiency and improving both physical and mental well-being.
High-Quality Protein for Muscle Strength and Testosterone Production
- Lean red meat, poultry
- Tofu, legumes
Protein matters because your body uses amino acids to repair muscle tissue, support metabolism, and make new hormones. Insufficient protein intake can lead to reduced muscle mass and ultimately lower testosterone. Quality sources — lean red meat, poultry, tofu, beans, and lentils — should feature in at least one or two meals per day, supplying the full spectrum of amino acids your body needs. Studies have shown that healthy men and women with higher protein diets, especially those who also engage in regular exercise or resistance training, maintain better muscle strength and more stable hormone levels. For vegetarians or vegans, variety is key: combining legumes and seeds ensures you hit your protein and micronutrient needs for healthy testosterone balance.
The synergy of protein with healthy fats and minerals forms a robust foundation for anyone aiming to increase testosterone naturally, powering you through workouts, daily demands, and helping stave off the unwanted effects of testosterone deficiency.
| Best Food | Key Nutrients | Effect on Testosterone |
|---|---|---|
| Salmon, Mackerel | Omega-3s, Healthy Fats | Boosts testosterone and reduces inflammation |
| Oysters | Zinc, Protein | Increases testosterone production |
| Egg Yolks | Cholesterol, Vitamin D | Supports hormone synthesis |
| Pumpkin Seeds | Magnesium, Zinc | Aids hormone balance, supports muscle function |
| Lean Beef | High-Quality Protein | Preserves muscle and metabolism |
| Legumes, Tofu | Plant Protein, Minerals | Supports testosterone in plant-based diets |
What Lowers Testosterone: Dietary Traps to Avoid
Not all foods are created equal when it comes to testosterone production. In fact, certain foods and dietary patterns can actively lower testosterone, slow metabolism, and drain energy. The biggest culprits are processed foods, excess added sugar, trans fats, and foods with excessive artificial additives. Consuming these foods regularly can lead to metabolic syndrome, unwanted weight gain, unstable hormone levels, and increased risk of chronic illness. That’s why steering clear of junk foods is as essential as seeking out testosterone-boosting nutrients.
Avoiding these problems begins with reading ingredient labels, choosing whole over processed, and keeping alcohol in moderation. The following sections highlight common traps and myths, plus evidence-based ways to sidestep foods that reduce your levels of testosterone.
Processed Foods and Added Sugar Reduce Testosterone Levels
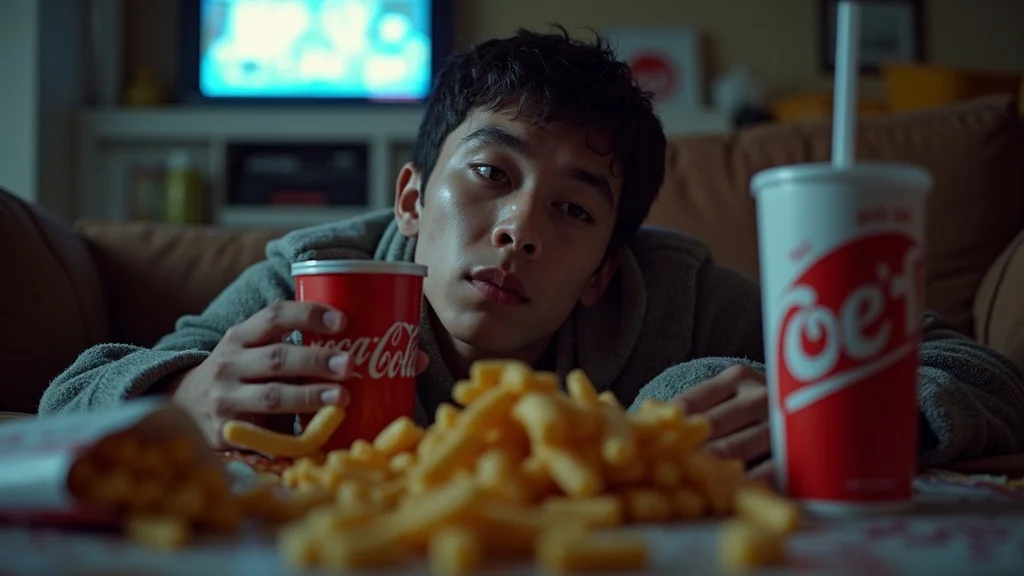

Mounting research points to the impact of sugar and processed foods on testosterone level. Diets high in white bread, pastries, fried snacks, and sugary drinks are linked to lower testosterone, fatigue, and mood swings in both healthy men and women. These foods don’t just provide empty calories—they can actively raise inflammation, choke hormone production, and worsen symptoms of testosterone deficiency, including low sex drive and poor muscle strength. The takeaway: If you’re looking for ways to increase and sustain your testosterone levels, ditching sweetened sodas and processed meals is a must.
Swapping out these traps for consistently nourishing foods will not only help increase your total testosterone, but you’ll see benefits in your energy, weight management, and long-term health — crucial for anyone who wants vibrant aging and a robust body at every stage of life.
Soy, Flaxseed, and Alcohol: Do They Lower Testosterone?
There’s much debate about whether soy and flaxseed lower testosterone. In men, excessive consumption of soy products may influence testosterone production due to phytoestrogens (plant-based estrogen mimics), but moderate intake as part of a balanced diet or plant-based meal plan doesn’t appear to have significant negative effects for most people. Flaxseed, high in lignans, has been shown in some cases to reduce testosterone, but mostly in very large supplemental doses. Alcohol, particularly when consumed in large or regular amounts, is a known testosterone disruptor; it can lower serum testosterone and drive up hormones like cortisol that undermine muscle mass and energy. Moderation — or mindful avoidance — is key for anyone seeking optimal hormone levels.
Context and quantity matter. Enjoy a balanced variety of foods, limit alcohol, and focus on what you can add to your routine, not just what to cut. This approach sustains motivation and supports healthier testosterone levels in the long run.
Trans Fats, Excessive PUFA Intake, and Hormone Disruptors
Trans fats are notorious for their ability to negatively impact hormone production and reduce testosterone. They’re common in fried snacks, processed pastries, and some commercial baked goods. Excessive polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) — especially from processed vegetable oils — can disrupt hormone levels if not balanced with healthy omega-3s. Artificial additives present in many snack foods further complicate your body’s regulation of sex hormone and metabolism.
- Refined sugars and grains
- Highly processed snacks
- Alcohol in excess
- Foods with artificial additives
To protect your testosterone production and support a healthy, active life, build your meals around whole ingredients and keep chemical-laden foods to a minimum. Small tweaks now mean fewer problems with declining testosterone levels in the years ahead.
Meal Plans: Structuring a Day’s Diet for Testosterone Production
The right daily meal structure can amplify all the benefits of a diet for testosterone production. Prioritize whole foods, combine healthy protein with quality fats and slow-digesting carbohydrates, and space your meals to maintain balanced hormone levels throughout the day. Below you’ll find a sample meal plan—easy to adapt for personal taste—that will help you start strong, stay energized, and recover well, whatever your training or daily routine looks like.
Making your meals predictable—yet varied in color and nutrient content—helps establish the nutritional foundation your body needs to boost testosterone every day, for both men and women.
Sample Meal Plan: Boost Testosterone Through Balanced Meals
- Breakfast: Eggs, avocado, spinach
- Lunch: Grilled salmon, quinoa, broccoli
- Snack: Pumpkin seeds, yogurt
- Dinner: Lean beef stir-fry with peppers and olive oil
This sample meal plan combines all the core testosterone-enhancing nutrients — from eggs and fatty fish for healthy fats and vitamin D, to nuts and lean beef for protein, zinc, and magnesium. Each meal features a balance of whole food carbs (like quinoa and greens), supporting muscle strength and steady energy. The moderate snack of pumpkin seeds and yogurt delivers minerals and beneficial bacteria for gut health, also implicated in hormone balance. This structure isn’t just effective—it’s delicious and sustainable, helping you easily stick to habits that increase testosterone levels over time.

Meal Timing and Frequency: Does It Affect Testosterone Levels?
Meal timing — when and how often you eat — can influence your testosterone levels, but quality and consistency count for more than any single timing trick. Some research demonstrates that eating a protein-rich breakfast and avoiding large nighttime meals help stabilize hormone production and boost testosterone in the morning, when natural release peaks. For others, intermittent fasting or eating within a defined window may offer metabolic benefits, but care must be taken not to under-eat or skip nutrients, which can negatively impact hormone production.
Regardless of specific timing, avoid prolonged or strict calorie restriction, as this often leads to lower testosterone and diminished muscle mass. The most reliable advice: eat regular, balanced meals, keep portions moderate, and adjust meal frequency based on activity level and hunger cues. Pay attention to how your body—and your mood—responds, and stay hydrated. Consistency and overall nutrient density win every time.
Supplements for Testosterone Production: Do You Need Them?

While nothing replaces a nutrient-rich diet, supplements can fill crucial gaps in your diet for testosterone production, especially if you’re deficient in key nutrients. Strategic supplementing with vitamin D, zinc, or magnesium may be beneficial for those struggling to get enough through food alone or during times of increased stress or activity. Not all supplements are created equal, though — the form and bioavailability matter for how well your body can absorb them.
If you’re considering supplements, focus on well-absorbed forms such as liquids, nano-drops, or quantum strips, which bypass many absorption issues of traditional pills or tablets. Always pair supplements with whole food choices for the best effect on your testosterone levels, energy, and overall wellness. Consult with your healthcare provider before starting new supplements, particularly if you have underlying health conditions or take other medications.
Choosing Bioavailable Options: Liquids, Nano-Drops, and Quantum Strips
Scientific advances have brought a new generation of supplements—liquids, nano-drops, quantum strips—that offer much higher absorption rates than standard capsule or pill formats. Because your body absorbs these forms rapidly and completely, you may notice faster effects on testosterone level, energy, and resilience. These high-tech options are especially worthwhile for nutrients like vitamin D, magnesium, and some herbal extracts, where absorption can be a limiting factor. For individuals with digestion issues or trouble swallowing pills, they’re a game changer, supporting consistent hormone production without unnecessary additives or fillers.
Prioritize supplements with transparent ingredient lists, and look for third-party testing to ensure quality and potency. When paired with a robust balanced diet and regular exercise, these bioavailable formats can help optimize testosterone production and support your vitality at any age.
Popular Supplements: Tribulus, Ashwagandha, Fenugreek & Their Efficacy
Several herbal supplements gain attention for their potential to increase testosterone, but evidence varies. Tribulus terrestris, Ashwagandha, and Fenugreek are the best-researched — some studies report moderate benefits in raising serum testosterone levels, improving muscle strength, and reducing stress (which can otherwise suppress testosterone). They’re most effective when used to address specific deficiencies or as part of a total health regimen — not as solo solutions. Evaluate products carefully: standardized extracts with clinical backing are best. Combine any herbal support with lifestyle changes and, ideally, under medical supervision for the safest and most sustainable approach to supporting healthy testosterone levels.
Remember, whole foods remain the gold standard for long-term health and sustained testosterone production — supplements are just that: supplemental to an already-rich, balanced routine.
| Nutrient | Best Food Source | Top Supplement Form | Absorption/Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D | Egg yolks, fortified milk, sunlight | Liquid drops, nano-absorbable strip | High absorption, boosts free testosterone |
| Zinc | Oysters, pumpkin seeds | Gluconate or picolinate liquid | Crucial for hormone synthesis |
| Magnesium | Nuts, seeds, leafy greens | Liposomal liquid, nano complex | Muscle and nerve support, balances hormones |
| Ashwagandha | Herbal root powder | Bioavailable extract strip | Lowers stress, may increase testosterone |
Expert Tips to Increase Testosterone Naturally (Foods, Habits, Lifestyle)
- Prioritize sleep
- Increase resistance training
- Maintain healthy body fat levels
- Manage stress for cortisol control
Beyond nutrition, a few core habits can further boost testosterone and satisfy your body’s natural hormonal needs. Prioritize seven to eight hours of deep sleep nightly — research confirms poor sleep drastically reduces testosterone, especially in active adults. Add regular resistance training (like weightlifting or bodyweight workouts); it’s proven to raise total testosterone, muscle mass, and resilience at any age. Keep body fat in check — excess adiposity raises estrogen and hinders testosterone production. Finally, stress management is crucial: high cortisol both blocks testosterone creation and promotes break down of muscle mass. Meditation, yoga, daily walks, and mindful breathing protect both mind and hormones, making the most of any improvements you make in diet.

People Also Ask: Diet for Testosterone Production
What diet produces the most testosterone?
A diet that produces the most testosterone focuses on whole foods rich in healthy fats, zinc, vitamin D, quality protein, and limits processed foods, sugar, and alcohol. Examples include Mediterranean and paleo-style diets.
How can I get 1000 testosterone naturally?
Maximize natural testosterone by combining nutrient-rich foods (fatty fish, eggs, nuts), regular strength exercise, good sleep, and stress reduction. Individual results will vary; 1,000 ng/dL is high and should be approached with holistic lifestyle changes.
Do eggs increase testosterone?
Eggs, especially the yolks, are a good source of cholesterol and vitamin D — both support testosterone production. Including eggs in moderation as part of a balanced diet for testosterone production can be beneficial.
How can I raise my testosterone level quickly?
Quick results may come from optimizing sleep, reducing sugar and processed foods, engaging in intense physical activity, and consuming key testosterone-boosting foods like fatty fish, nuts, and leafy greens.
FAQs: Diet for Testosterone Production
-
Can women benefit from a diet for testosterone production?
Absolutely. While women produce less testosterone, this hormone is vital for their energy, bone health, mood, and muscle tone. A targeted diet supports healthy levels and overall wellness. -
How fast can dietary changes improve testosterone levels?
Improvements are often seen in 4–6 weeks, particularly when paired with better sleep and exercise. Results depend on age, baseline health, and consistency. -
Should older adults focus more on testosterone-boosting diets?
Yes. As testosterone naturally declines with age, older adults—both men and women—benefit from a nutrient-rich diet to support longevity, mobility, and cognitive clarity. -
Are there risks to increasing testosterone through diet?
If you focus on whole foods and moderate intake, risks are minimal. However, extreme dietary interventions or unregulated supplements require caution and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Key Takeaways: Diet for Testosterone Production
- Balanced nutrition is fundamental for testosterone health.
- Both men and women can benefit from a targeted diet.
- Avoid processed foods and prioritize whole-food nutrients.
- Consider supplements if dietary intake is lacking.
- Lifestyle factors — sleep, stress, exercise — multiply the impact of dietary changes.
Maximize Results: Taking Action With Diet for Testosterone Production
💧 Want to feel the difference absorption makes? See the supplements we recommend for maximum impact — and why liquids, nano-drops, and quantum strips work better.👉 [Discover Our Top Picks →]
Conclusion
Optimizing your diet for testosterone production empowers both men and women to live with more energy, resilience, and joy—naturally. Invest in whole foods, smart supplementation, and sustaining habits to unlock your body’s full hormonal potential for the long haul.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment