Have you ever wondered if your choice of olive oil truly matters for your health? With so many claims about pressed olive oil and extra virgin olive oil in the spotlight, it’s time to cut through the confusion and discover what science—and centuries of Mediterranean tradition—really say about cold pressed olive oil. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore why this golden oil is hailed as a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet, outline its top 10 health benefits, and reveal if cold pressed olive oil lives up to the wellness hype.
Is Cold Pressed Olive Oil Healthy? An Intriguing Look at Mediterranean Wisdom
The question, “Is cold pressed olive oil healthy?” is at the heart of nutritional debates and culinary traditions worldwide. Rooted in deep Mediterranean wisdom, cold pressed and extra virgin olive oil have been central to diet and lifestyle in regions where heart disease rates are among the lowest globally. Studies have shown that regular consumption of olive oils—especially those labeled as first cold press or extra virgin olive oil—correlates with longevity, lower risk of heart disease, and overall improved wellness. But what exactly elevates these oils above standard varieties?
Unlike highly processed or refined oil, cold pressed olive oil is created through a careful, low-temperature extraction that protects natural phytonutrients and healthy fats. This means you aren’t just adding flavor to your salads and pastas; you’re fueling your body with monounsaturated fats, antioxidants, and a potent mix of polyphenols. These compounds don’t just play a role in heart health—they offer protection against inflammation and may even help regulate cholesterol levels. As we examine the science and the enduring use of olive oil in the Mediterranean diet, it’s clear why this oil has earned a reputation as a functional superfood and why so many health-conscious individuals are making the switch.

What You’ll Learn About Cold Pressed Olive Oil and Health
- What makes cold pressed olive oil unique
- Top 10 health benefits of first press extra virgin olive oil
- Comparisons between cold pressed, virgin, and extra virgin olive oil
- Potential side effects and disadvantages
- How cold pressed olive oil fits into a healthy diet
Understanding Cold Pressed Olive Oil: Origin and Extraction
What Does 'Cold Pressed' Mean in Olive Oil?
‘Cold pressed’ refers to a method where olive oil is extracted by mechanical means at temperatures below 27°C (80°F), ensuring delicate nutrients and aromatic compounds remain intact. This gentle process, also called first cold pressing, involves crushing fresh olives and slowly pressing them without heat or chemicals for the purest oil possible. The result is more than a culinary delight; it’s a nutrient-rich oil bursting with health benefits. By avoiding high temperatures, cold pressed olive oil preserves flavor, antioxidants, vitamins, and the integrity of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids—key contributors to its acclaimed heart health properties and low saturated fat content. In contrast, regular olive oil may come from a blend of cold pressed and refined oil, which can diminish beneficial fatty acids like oleic acid and valuable vitamins. The difference in process is what makes cold pressed olive oil so appealing for those who value the highest grade and most natural product for long-term wellness.
This method is a cornerstone in producing extra virgin olive oil, the highest standard among olive oil types. Both cold pressed and extra virgin olive oil are celebrated for their high level of polyphenols and a unique balance of unsaturated fatty acids, helping protect the body against oxidative stress and inflammation. For centuries, Mediterranean households have trusted this process for both flavor and well-being, confirming what modern nutritional science now validates.
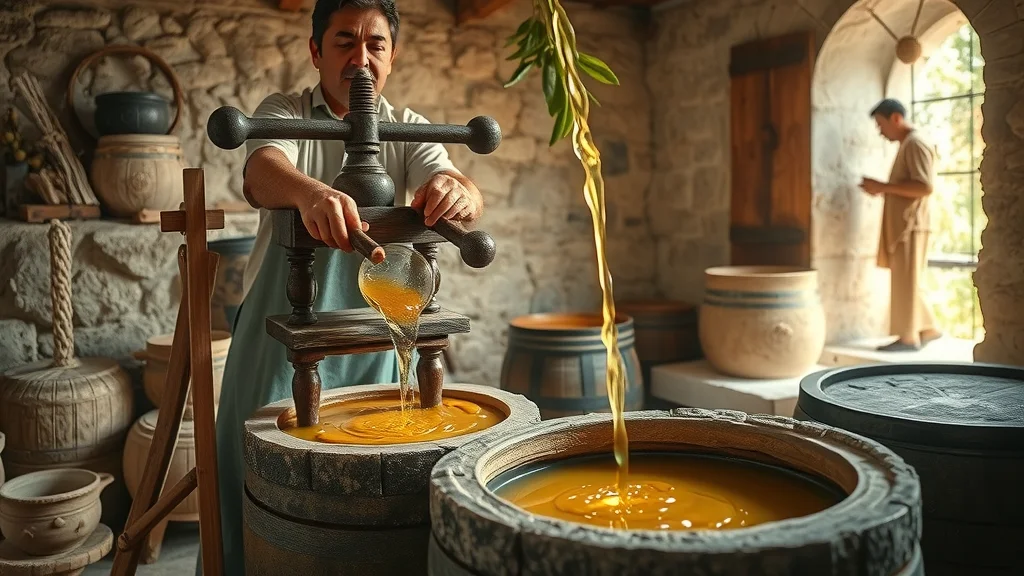

How Cold Pressed Olive Oil Differs from Regular Olive Oil
When comparing cold pressed olive oil to regular olive oil, the distinctions go far beyond taste. First, cold pressed oil is extracted without heat or chemicals, while regular olive oil often involves refined oil, where higher temperatures may break down antioxidants and essential fatty acids. The chemical and nutritional differences are significant: cold pressed and extra virgin olive oil boast higher amounts of beneficial polyphenols, lower acidity (often below 0.8%), and maintain natural flavors and aromas. In contrast, regular or refined olive oils can lose much of their nutritional potency through industrial processing, reducing both their health benefits and distinctive taste.
- Extraction temperature and process: Cold pressed oils are processed below 27°C, protecting nutrients. Regular refined oils are often heated, leading to nutrient loss.
- Chemical and nutritional differences: Cold pressed and extra virgin olive oils are rich in monounsaturated fats, antioxidants, and polyphenols, while regular olive oils may lack these compounds due to processing.
- Taste and aroma comparison: Cold pressed oils have a peppery, fruity, complex aroma, whereas regular olive oils are milder and sometimes bland due to refining.
This crucial difference not only impacts your culinary experience but fundamentally alters the oil’s health profile. If you’re seeking the benefits promoted in studies of the Mediterranean diet and heart health, cold pressed and extra virgin are the superior choices.
For those interested in how dietary fats like olive oil can influence broader health outcomes, including fertility and long-term wellness, you may find it insightful to explore the global trends and health implications discussed in this analysis of global fertility declines and their impact on future health. Understanding these connections can help inform smarter dietary choices.
Nutritional Profile: Is Cold Pressed Olive Oil Healthy?
Key Nutrients in Cold Pressed and Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Cold pressed and extra virgin olive oil stand out nutritionally among cooking oils due to their unique fatty acid profiles and antioxidant content. One of their main strengths is a high level of monounsaturated fat, specifically oleic acid (roughly 73g per 100g). This fatty acid is renowned for lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol while raising HDL (good) cholesterol, contributing significantly to heart health and reducing the risk of heart disease. In addition, first press olive oil contains Vitamin E, a potent antioxidant that supports skin and cellular health, and polyphenols that fight inflammation on the cellular level.
Despite being a fat, olive oil is light on saturated fat compared to animal-based options and other common cooking fats, promoting a heart-healthy profile recommended by numerous dietary guidelines. While small amounts of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are present, the star nutrients remain the unsaturated fats and antioxidants, which combine to offer both flavor and robust health benefits.
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g | Health Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Monounsaturated Fats | 73g | Heart health, cholesterol balance |
| Vitamin E | 14mg | Antioxidant, skin health |
| Polyphenols | Varies | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant |
| Omega-3 & 6 | Minimal | Cell structure, heart protection |
Role of Polyphenols and Antioxidants in Cold Pressed Olive Oil
A standout feature of cold pressed olive oil is its concentration of polyphenols and antioxidants. These powerful plant compounds are responsible for many of the oil’s acclaimed health benefits. Scientific research indicates that polyphenols help neutralize oxidative stress, a major contributor to chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer. They reduce inflammation throughout the body, further enhancing heart health, and are instrumental in protecting blood vessels and supporting overall cardiovascular wellness. Studies have shown that diets high in polyphenol-rich olive oil, such as the Mediterranean diet, can significantly lower the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
The antioxidant properties aren’t just relevant for disease prevention. Antioxidants like Vitamin E and hydroxytyrosol also help keep the oil stable, delaying rancidity when stored correctly. For anyone considering pressed olive oil as a daily health staple, these natural protectors offer both immediate and long-term benefit—helping your cells recover from everyday stress while supporting lasting vitality.
Top 10 Health Benefits of Cold Pressed Olive Oil: Mediterranean Diet Proof
Scientific studies and age-old Mediterranean tradition consistently highlight the remarkable health benefits of cold pressed olive oil and extra virgin olive oil. When incorporated as the main fat source in a balanced diet, here are the top 10 benefits you can expect:
- Reduces risk of heart disease (proven in Mediterranean diet studies)
- Lowers inflammation throughout the body
- Improves cholesterol levels (boosts HDL, lowers LDL)
- Supports healthy brain function and reduces risk of stroke
- Aids in weight management when used moderately
- Enhances skin health and slows aging
- Promotes gut health and digestive function
- May reduce risk of diabetes
- Provides strong antioxidants to fight oxidative stress
- Supports bone density and joint health
“The Mediterranean lifestyle, anchored by daily use of first press extra virgin olive oil, continues to set the gold standard for lifelong health.” – Renowned Mediterranean Diet Researcher
Why Mediterranean Cultures Trust First Press Olive Oil
Mediterranean communities have relied on first press cold pressed olive oil for generations, using it in everything from rustic dips to elaborate celebratory feasts. Their trust is built on more than flavor—it's a legacy of health that’s visible in their longevity statistics and low rates of heart disease. Scientific research frequently references the so-called “Mediterranean paradox”—high consumption of fat, but the healthiest populations. The key is the type of fat: the monounsaturated fats and antioxidants found uniquely in cold pressed and extra virgin olive oils. Mediterranean elders credit their daily spoonful of golden oil as a reason for their vitality and resilience.
In these cultures, olive oil is regarded not just as a cooking fat, but a fundamental “superfood” integrated into daily life. The wisdom of their approach is now globally recognized—and increasingly validated by Western scientists who confirm its ability to reduce risk of heart disease, lower inflammation, and support a healthy lifespan.

Cold Pressed vs. Extra Virgin Olive Oil vs. Regular Olive Oil
Understanding Olive Oil Grades: Virgin, Extra Virgin, and Refined
Not all olive oils are created equal. Understanding the grades helps clarify which type delivers the full spectrum of health benefits:
- Cold pressed olive oil: Made from first mechanical pressing of fresh olives at low temperatures; preserves antioxidants, polyphenols, and healthy fatty acids.
- Virgin olive oil: Slightly higher acidity; still natural and unrefined, but with minor flavor differences.
- Extra virgin olive oil: The highest grade with low acidity (<0.8%), exceptional flavor, and the richest in nutrients and health-promoting compounds.
- Regular olive oil: Typically a blend of refined and virgin oils. Refining reduces antioxidants, healthy fats, and flavor complexity.
Extra virgin and cold pressed olive oils truly set themselves apart through their superior nutrient content and robust flavor profiles. For the maximum health benefits and authentic taste reminiscent of the Mediterranean, always reach for “extra virgin,” “cold pressed,” or “first press” on the label.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil vs. Cold Pressed: Is There a Difference?
Many shoppers wonder if ‘cold pressed’ and ‘extra virgin olive oil’ are the same thing. While they are closely related, extra virgin is a grade based on taste, chemistry (acidity below 0.8%), and method, whereas ‘cold pressed’ describes the method of extraction. Nearly all true extra virgin olive oil is cold pressed, so the best products boast both descriptors. This combination means you get the oil at its freshest, packed with polyphenols, oleic acid, and a high level of heart-protective unsaturated fats—a key to the Mediterranean diet’s success. Always verify the bottle labels for both terms for optimal quality and authenticity.
It’s easy to see why the best pressed olive oils are cherished not only for flavor but also for their science-backed ability to reduce inflammation, promote heart health, and protect against chronic disease. If you’re seeking to maximize health benefits, extra virgin cold pressed olive oil is the gold standard.
Pressed Olive Oil and Pressed Olive: Are They as Healthy?
The terms “pressed olive oil” and “pressed olive” can cause confusion. In nutritional terms, pressed olive oil—meaning oil that’s extracted from olives mechanically and without excess heat—carries the highest health benefits. Commercial “pressed olive” or “light olive oil” may be more refined and lack the nutrients that make the first press or cold pressed oil so potent. Always prioritize oils labeled cold pressed or extra virgin for the highest concentration of antioxidants, polyphenols, and healthy monounsaturated fats, as found in trusted Mediterranean traditions.
With these distinctions, you’ll know precisely how to choose for the greatest health impact and enjoy the rich, fruity notes of top-grade olive oil in every meal.
Potential Disadvantages and Side Effects: Is Cold Pressed Olive Oil Always Healthy?
What Are the Disadvantages of Cold Pressed Oil?
Despite its impressive reputation, cold pressed olive oil does have some limitations to keep in mind:
- Prone to rancidity if not stored properly
- Higher price point than refined oils
- Potential for adulteration or mislabeling
The high content of natural antioxidants in pressed olive oil helps delay spoilage, but because it’s not treated with preservatives, it’s important to store it in a cool, dark place, ideally in dark glass bottles. This preserves its flavor and health benefits. Its artisanal, high-quality extraction methods also mean it costs more than regular olive oil, but the investment is often justified by superior taste and nutrition. Lastly, due to its popularity, it’s crucial to check for credible certification and origin to avoid misrepresentation—especially important for extra virgin labels.
What Are the Side Effects of Cold Pressed Olive Oil?
For most individuals, cold pressed olive oil is safe and well-tolerated. However, a few potential side effects exist:
- Mild digestive upset in rare cases
- Possible allergic reactions (extremely rare)
- High-calorie content to consider for weight management
While cold pressed olive oil is healthy, consuming excessive quantities could contribute to unwanted weight gain due to its calorie density (about 120 calories per tablespoon). If you’re new to pressed oils, introduce them gradually to your diet to minimize the risk of mild digestive upset. True allergies to olive oil are exceedingly rare, but as with any natural product, discontinuing use if any reaction occurs is wise.

Special Considerations: Is Olive Oil Good for Early Pregnancy?
Pregnant individuals often seek the healthiest choices for both themselves and their developing baby. Several studies, alongside centuries of Mediterranean tradition, suggest that moderate consumption of cold pressed and extra virgin olive oil during early pregnancy can offer important nutrients, including Vitamin E and healthy monounsaturated fats. These nutrients promote brain and cellular development for the fetus and support maternal health by reducing inflammation and aiding digestion. The oil’s rich polyphenol content and low level of saturated fat make it an excellent choice for heart-supportive nutrition during pregnancy. However, as with all dietary changes, it’s best to consult a healthcare provider to tailor intake to individual needs.
Including a small amount (one to two tablespoons) daily, as a salad dressing or drizzle, can help ensure optimal nutrient absorption and provide a delicious, safe fat source during this critical time.
How to Incorporate Cold Pressed Olive Oil Into Your Diet
Ways to Enjoy Cold Pressed Olive Oil Daily
Bringing the health benefits of cold pressed olive oil into your everyday meals is simple, delicious, and in line with Mediterranean culinary habits. Here are some effortless and tasty ways to get your daily dose of antioxidants and healthy fats:
- Drizzle on salads and fresh vegetables
- Use as a finishing oil for soups or pastas
- Substitute in baking for a healthier fat
- Mix into dips and spreads
These versatile uses mean you don’t have to overhaul your diet—just tweak your choices at meal times to mirror the patterns of the world’s healthiest cultures.

Tips for Choosing Genuine, Healthy Cold Pressed Olive Oil
- Look for certification seals (PDO, PGI, COOC)
- Opt for dark glass bottles and harvest dates
- Understand product labeling (extra virgin, virgin, first cold pressed)
The healthiest choice will always be cold pressed or extra virgin olive oil with clear labeling, recent harvest dates, and stored in dark or opaque bottles. Quality certifications ensure authenticity and higher polyphenol content, safeguarding you from misleading claims—helping you harness all the nutritional power this oil can offer.
People Also Ask: Is Cold Pressed Olive Oil Healthy?
Is cold-pressed olive oil healthier?
Yes, cold-pressed olive oil is generally healthier because it’s processed at low temperatures that preserve its antioxidants, vitamins, and monounsaturated fats. This enhances its heart protective, anti-inflammatory, and cholesterol-balancing benefits compared to refined or regular olive oil. Using cold pressed or extra virgin olive oil as your main dietary fat can help lower the risk of heart disease and improve overall well-being. Research supporting the Mediterranean diet emphasizes these health advantages.
What are the disadvantages of cold pressed oil?
The main disadvantages of cold pressed olive oil are its higher price point, greater susceptibility to rancidity if left in light or heat, and the risk of mislabeling in the market. However, these are often minor concerns in light of the significant health benefits provided the oil is sourced and stored properly. Always check for certification, optimal packaging, and freshness to avoid these issues.
What are the side effects of cold pressed olive oil?
The vast majority of people tolerate cold pressed olive oil well, but very large amounts can contribute to weight gain due to its calorie content. Rare side effects include mild digestive upset or allergies, but these are not common. Moderation and gradual introduction into your diet further minimize any issues.
Is olive oil good for early pregnancy?
Olive oil, especially cold pressed and extra virgin, is generally considered very good for early pregnancy thanks to its high content of Vitamin E and heart-healthy unsaturated fats. These nutrients play a role in fetal development and maternal health. As always, consult your doctor for tailored advice during pregnancy.
Educational video highlighting how cold pressed and extra virgin olive oil power the Mediterranean diet, with insights from nutritionists and researchers.
Key FAQs About Cold Pressed Olive Oil and Health
-
How much cold pressed olive oil should I consume daily?
About one to two tablespoons daily is recommended for optimal heart and overall health benefits. -
Does cold pressed olive oil lose benefits when cooked?
Some polyphenols are reduced with high heat, but most nutrients remain if used for gentle sautéing or drizzling on warm foods. -
How can I spot high-quality extra virgin olive oil?
Look for trusted certifications, dark bottles, fresh harvest dates, and clear “extra virgin” and “cold pressed” labels. -
Is there a difference in taste between regular and cold pressed olive oil?
Yes—cold pressed oils are robust, peppery, and fruity, while regular oils are milder with fewer complex aromas. -
Can cold pressed olive oil help reduce cholesterol?
Yes, studies show cold pressed olive oil can improve cholesterol by raising HDL and lowering LDL cholesterol levels.
Key Takeaways: Why Cold Pressed Olive Oil Is Still the Gold Standard
- Cold pressed olive oil combines tradition with nutritional excellence
- First press and extra virgin status ensure highest health benefits
- Mediterranean lifestyle and longevity are strongly linked to daily olive oil use
- Proper sourcing and storage are crucial to maximize benefits
Quotes from Experts and Mediterranean Nutritionists
“It is not just a food, but a preventive medicine woven into the daily life of Mediterranean cultures.” – Esteemed Mediterranean Nutritionist
“The extra virgin and first cold press olive oils are the most beneficial due to their superior polyphenol content.” – Dietary Science Specialist

Conclusion: Is Cold Pressed Olive Oil Healthy in Today’s Diet?
Incorporating cold pressed olive oil into your diet remains a science-backed, tradition-proven step toward lasting health—echoing the wisdom and wellness of Mediterranean cultures for centuries.
If you’re inspired by the role of nutrition in shaping not just personal health but also broader societal trends, consider delving into the far-reaching effects of dietary patterns on population well-being. Our in-depth feature on global fertility declines and the opportunities for a healthier future offers a strategic perspective on how lifestyle choices, including what we eat, can influence generational health outcomes. By connecting the dots between individual habits and global health shifts, you’ll gain a richer understanding of how mindful nutrition—like choosing high-quality olive oil—can be a catalyst for positive change. Take the next step in your wellness journey and explore how your daily choices contribute to a healthier world.
Ready to Transform Your Health?
💧 Want to feel the difference absorption makes? See the supplements we recommend for maximum impact. 👉 Discover Our Top Picks →
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment