Did you know? By the time you hit your 40s, your testosterone levels can quietly slip by as much as 1% a year—setting off a ripple effect that influences energy, focus, muscle strength, and the very way you age. Testosterone and aging go hand in hand, affecting men and women in ways that can shape vitality for decades.
The Surprising Link Between Testosterone and Aging
"By age 40, testosterone levels in men can decline by up to 1% per year—a silent force shaping how we age."

Why Testosterone Matters for Both Men & Women
People often see testosterone as a “man’s hormone,” but this couldn’t be further from the truth. Testosterone is a sex hormone that plays a vital role in health for both men and women. In men, the hormone powers muscle mass, bone density, and mood, but in women, too, it underpins energy, confidence, libido, and even bone health—especially after menopause. As we age, declining testosterone levels subtly change our bodies and minds, influencing everything from energy to focus and motivation. Addressing testosterone and aging for both men and women means looking at hormonal balance as foundational to vitality, not just as a “male issue.” Supporting optimal levels leads to greater resilience, sharper thinking, and a more youthful outlook—inside and out.
- Testosterone and aging: impacts energy, muscle mass, bone density, and mental sharpness
- Low testosterone: affects both men and women
- Growing trend: natural options for supporting testosterone levels
What You'll Learn About Testosterone and Aging
- How testosterone impacts aging in men and women
- Science behind testosterone production and leydig cell function
- Symptoms and risks of low testosterone levels
- Natural ways to support healthy testosterone levels
- When to consider testosterone replacement or therapy

Understanding Testosterone and Aging: The Science
Testosterone Level Decline: Patterns and Timeline
Testosterone levels naturally peak in early adulthood and begin a gradual, almost invisible decline with age. For men, the drop averages about 1% per year after 30 or 40. But women are affected too—though typically at about one-tenth the levels of men, their hormone drop accelerates after menopause. This decline in testosterone can set the stage for a variety of aging symptoms: loss of muscle mass, reduced bone density, dips in mental sharpness, and mood changes. Understanding when and how testosterone and aging connect helps pinpoint the years when you’ll want to pay special attention to symptoms or risk factors. Tracking levels of testosterone regularly—especially if you notice fatigue, strength loss, or mood swings—can help you stay ahead of unwanted changes and support healthy hormone balance over time.
| Age Group | Men (ng/dL) | Women (ng/dL) |
|---|---|---|
| 20–29 | 300–1,000 | 15–70 |
| 30–39 | 270–900 | 13–65 |
| 40–49 | 230–830 | 10–60 |
| 50–59 | 200–750 | 7–55 |
| 60+ | 170–700 | 5–45 |
Leydig Cell Function and Testosterone Production
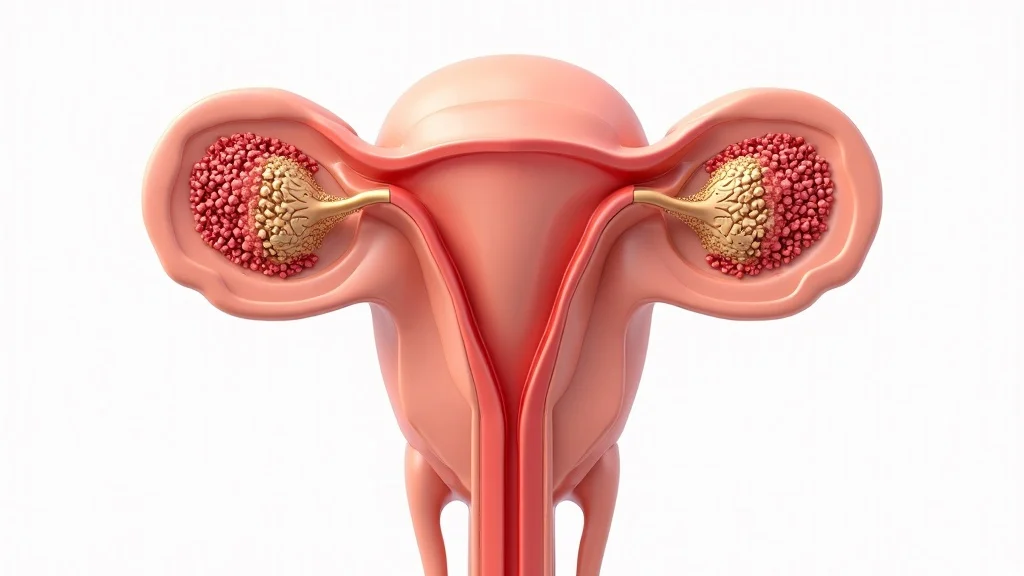
The key to healthy testosterone production lies in the leydig cells—specialized cells in the testes (for men) and ovaries/adrenal glands (for women). When stimulated by luteinizing hormone, leydig cells manufacture testosterone from cholesterol, sending it throughout the body to influence muscle strength, bone density, and energy. Over time, leydig cell health can decline as part of the natural aging process. Exposure to toxins, oxidative stress, and chronic inflammation may accelerate this loss, contributing to lower testosterone levels and a cascade of age-related challenges. Research continues to explore how diet, exercise, and lifestyle factors can help support leydig cell function, preserve testosterone production, and delay unwanted aspects of aging.
The Role of Testosterone in Maintaining Muscle Mass and Bone Density
Testosterone isn’t just about sexual function or libido—it is critical for building and maintaining healthy muscle mass and bone density. In both men and women, normal levels of testosterone contribute to muscle strength, faster recovery after workouts, and protection against osteoporosis. As testosterone drops, older men and women often experience a slow, persistent loss of lean muscle and a higher risk of bone fractures. This connection is so strong that men with low testosterone and postmenopausal women are specifically monitored for osteoporosis. Recognizing these links earlier means you can act—through exercise, diet, or treatment—to preserve your strength and independence as you age.
- Loss of muscle mass
- Reduced bone density
- Decline in libido
- Mood & cognitive changes
Why Testosterone is Essential for Well-Being at Any Age
"Testosterone is not just a 'male hormone'—it is the cornerstone of strength, focus, and emotional vitality in both sexes."
Low Testosterone: Signs, Symptoms, and Early Detection
Many adults dismiss signs of low testosterone as “just getting older.” Yet symptoms such as fatigue, mood swings, decreased muscle mass, memory issues, and reduced motivation can signal that your body’s testosterone and aging cycles have veered out of balance. Both men and women can experience these symptoms when testosterone levels decline, and early signs may even appear in your 30s or 40s. Recognizing the early warning signs gives you a head start, allowing for lifestyle changes or testing that can restore energy, focus, and vitality before more severe muscle loss or bone weakening sets in. If you’re questioning your stamina, mood, or sex drive, ask if testosterone could be the missing piece to your wellness puzzle.
- Fatigue
- Mood swings
- Decreased muscle mass
- Memory lapses
- Reduced motivation
Testosterone Levels in Men vs. Women Across the Lifespan
Testosterone levels follow different, yet overlapping, patterns for men and women. Men start with substantially higher amounts of both total testosterone and free testosterone, but levels decrease gradually with age, contributing to classic aging symptoms. In women, testosterone is present in smaller doses, but the decline tends to accelerate after menopause, compounding the effects of drops in estrogen and progesterone. Across both genders, changes in levels of testosterone can impact everything from muscle strength and bone mass to sexual function, mood, and memory—making hormone health a cornerstone of vibrant aging. Monitoring changes by decade helps identify when lifestyle adjustments or treatment may offer the most benefit.
| Decade | Men: Avg. Level (ng/dL) | Women: Avg. Level (ng/dL) | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30s | 270–900 | 13–65 | Peak energy, early muscular changes |
| 40s | 230–830 | 10–60 | Fatigue, mood changes, slower recovery |
| 50s | 200–750 | 7–55 | Sexual function decline, bone loss, brain fog |
| 60s+ | 170–700 | 5–45 | Muscle weakness, osteoporosis, low libido |

Factors Affecting Testosterone and Aging
Lifestyle & Environmental Influences on Testosterone Levels
Your daily choices play a powerful role in shaping testosterone and aging—from what you eat, to your movement habits, sleep, and even the air you breathe. A balanced diet rich in protein, healthy fats, and micronutrients supports hormone production and leydig cell health. Regular exercise, especially strength or HIIT, stimulates natural testosterone production and helps maintain muscle mass. On the flip side, chronic stress, poor sleep, and frequent exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals can undermine testosterone levels for both men and women. By making small sustainable changes—improving sleep, reducing unnecessary toxins, and prioritizing physical activity—you help your body balance hormone production and protect long-term vitality.
- Diet & nutrition
- Exercise & sedentary habits
- Stress & sleep quality
- Exposure to endocrine disruptors
Age-Related Decline: Natural Versus Accelerated Drop

The rate at which testosterone levels decline is partly genetic, but can be greatly influenced by lifestyle. Natural aging brings a slow and steady reduction, but accelerated loss happens with obesity, diabetes, chronic illness, medication use, and excessive alcohol or tobacco. These risk factors may reduce leydig cell number and function, disrupt blood flow, or cause hormonal imbalances, leading to low testosterone symptoms much earlier than expected. Proactively managing modifiable factors—such as adopting a more active lifestyle, optimizing sleep, and managing stress—can slow the decline, preserving muscle mass and overall vitality even into later decades.
Genetic Factors and Leydig Cell Health
Genetics control some aspects of testosterone production and leydig cell health, but environment and lifestyle remain major influences. Some individuals simply have higher baseline testosterone, more robust leydig cells, or more sensitivity to luteinizing hormone. Others may inherit greater risk for hormone drops or related symptoms. Understanding your family health history alongside modern blood testing enables proactive steps, such as earlier screening or targeted natural support for testosterone and aging. While you aren’t able to change your genes, focusing on nutrition, movement, and toxin reduction ensures you give your leydig cells the best possible environment to continue healthy testosterone output throughout your lifetime.
Testosterone and Muscle Mass: Staying Strong As You Age
The Role of Testosterone in Maintaining Muscle Mass

Muscle mass is one of the most visible markers of aging—and one of the most closely tied to testosterone levels. As we age, particularly after 40, reduced total and free testosterone bring a reduction in muscle mass, muscle strength, and the speed at which we recover from exercise or injury. Maintaining higher levels helps older men and women preserve their independence, metabolism, and energetic appearance. Research on men with low testosterone shows a direct relationship between hormone levels and the development of sarcopenia—a syndrome of increased fat, declining strength, and frailty. Supporting healthy testosterone production through nutrition, exercise, and (when necessary) medical evaluation can slow and in some cases partly reverse muscle decline, helping maintain a vibrant, strong frame that sets the stage for healthy, active aging.
Training, Nutrition, and Testosterone: Strategies for Muscle Maintenance
Regular resistance training stimulates natural testosterone production and helps maintain or even increase muscle size, even as other aging processes march on. Pairing this with a protein-rich diet—combining lean meats, fish, dairy, legumes, and healthy fats—gives muscles and leydig cells the building blocks they need. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) has also been shown to boost testosterone in older men and women, while keeping metabolism high. Sleep can’t be overlooked: without 7–8 hours nightly, muscle tissue doesn't repair efficiently and testosterone levels can remain low. These strategies not only boost muscle (even for those with low testosterone) but also support bone density, help balance weight, and keep motivation and confidence high as you age.
"Adults with healthy testosterone levels retain more lean muscle mass and recover faster after exercise."
Low Testosterone Level and Sarcopenia: What to Watch For
Sarcopenia—the age-related loss of muscle mass and strength—is closely linked to low testosterone levels. In controlled trials, older men and women with the lowest testosterone saw faster declines in strength, endurance, and physical independence. Early signs of sarcopenia may include weakness, trouble with balance, and inability to keep up with peers in activities. Responding with targeted exercise and tailored nutritional support can slow or prevent progression. Natural interventions may help reverse some declines before considering hormone therapy. Knowing the connection between sarcopenia, testosterone, and aging makes it easier to proactively defend your muscle—and your quality of life.
| Testosterone Status | Muscle Mass | Recovery After Exercise | Long-Term Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Levels | Maintained | Fast | Active, independent |
| Low Levels | Reduced | Slow | Frailty, higher fall risk |

Bone Density, Testosterone, and Aging: Preventing Osteoporosis
How Testosterone Supports Strong Bones
Testosterone and bone density share a deep physiological link. This key sex hormone helps stimulate bone formation and maintain skeletal integrity in both sexes. Men who maintain healthy testosterone levels into older age are less likely to suffer osteoporosis or fractures. For women, the risk factor increases post-menopause, when both estrogen and testosterone levels plummet. Including weight-bearing and resistance exercises in your routine, getting adequate vitamin D and calcium, and discussing hormone levels with your healthcare provider are crucial steps to protecting your bones as you age.
Low Testosterone Levels and Osteoporosis Risk
Unchecked low testosterone levels are one of the silent causes of osteoporosis in older men and women. Postmenopausal women are at the highest risk, but men over 60 also suffer a slow, symptomless erosion of bone that can lead to sudden fractures from even minor falls. Fortunately, early detection and intervention can significantly reduce risk and support bone health for life. Prevention strategies include a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, regular screening, and discussion of hormone therapies if appropriate, especially if you are at increased risk based on family history or prior bone injuries.
- Post-menopausal women at highest risk
- Men over 60: silent decline in bone density
- Signs and prevention strategies
Mental Health, Mood, and Testosterone and Aging

Testosterone Level Fluctuations and Cognitive Function
Fluctuating testosterone levels have real impact on cognitive performance, memory, focus, and reaction time. Particularly in older men, very low testosterone levels may be linked to “brain fog,” slower thinking, or trouble finding words. Women, especially after menopause, may also notice mood or mental sharpness fade as hormone production decreases. Supporting healthy testosterone may help maintain or even improve certain aspects of cognition. Alongside brain-healthy habits—like learning new skills, meditation, and regular sleep—hormone health becomes an additional approach to keeping your mind and mood sharp through every decade.
Low Testosterone, Motivation, and Emotional Balance
Mood swings, anxiety, irritability, and lack of motivation often creep in as testosterone wanes with age—in both sexes. Some studies point to a role for testosterone in dopamine production, which helps regulate mood and motivation. These symptoms often overlap with fatigue and loss of muscle strength, making them easy to overlook. Early support, through stress management, targeted nutrition, or natural supplements, can help restore emotional balance and prevent dips in quality of life associated with hormone changes.
Testosterone Therapy and Quality of Life Improvements
For some, lifestyle changes and supplements are not enough to restore testosterone levels. In these cases, supervised testosterone therapy may make a world of difference—not just for sexual function, but for energy, mood, and motivation as well. Evidence from controlled trials shows that those with true hormone deficiency (testosterone deficiency or hypogonadism) can see marked improvements in mood, outlook, and day-to-day functioning with careful hormone replacement. However, testosterone therapy should always be approached conservatively, under the guidance of an expert, and reserved for those with documented low levels based on reliable lab tests.
Low Testosterone: Risks, Causes, and Comprehensive Solutions
Common Causes of Low Testosterone in the Aging Population
The most common reason for low testosterone is age-related decline in leydig cell function and sex hormone production. But chronic illness, such as diabetes, heart disease, and obesity, accelerates this drop. Poor lifestyle choices—insufficient sleep, low physical activity, high stress, environmental toxins, and certain medications—also contribute. For some, hormone replacement therapy or testosterone treatment may be necessary, but for most, lifestyle changes can help naturally balance testosterone and aging.
- Age-related leydig cell decline
- Chronic illness
- Poor lifestyle choices
- Medications
Detecting Low Testosterone Level: Diagnosis and Testing
If you experience signs like fatigue, loss of muscle or libido, or mood changes, consider asking your provider for a blood test measuring total testosterone, free testosterone, and sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG). These readings offer a full picture of hormone status. Timing your blood test in the morning provides the most accurate results. Further tests may check for underlying causes, including leydig cell health, blood sugar levels, or pituitary hormones (like luteinizing hormone). Using these insights, your doctor can recommend the most effective course of action—ranging from nutrition or fitness upgrades to medical therapies if needed.
Natural Methods to Support Healthy Testosterone Levels
Simple lifestyle changes remain the first line of defense for supporting testosterone production at any age. Resistance training, HIIT, heart-healthy fats (like avocados, nuts, and olive oil), and a diet low in processed foods each help maintain or boost leydig cell function. Minimizing exposure to endocrine disruptors—like BPA and phthalates—and managing chronic stress are equally vital. Natural supplements (including vitamin D, zinc, magnesium, and adaptogenic herbs) may offer additional support for those with borderline-low levels. These strategies can help preserve energy and confidence—and may delay or even prevent the need for medical testosterone replacement in many adults.
Testosterone Replacement & Therapy: Options for Aging Adults
When Is Testosterone Therapy Recommended?

Testosterone therapy is reserved for men and women with documented hormone deficiency and persistent symptoms not remedied by lifestyle changes alone. If you have consistently low levels confirmed by blood work and are struggling with fatigue, muscle loss, sexual dysfunction, or bone density problems, your doctor may discuss replacing what your body no longer produces. Individualized plans keep safety first—routine monitoring and the lowest effective dose are key to reducing risk factors and maximizing the benefits of therapy. Women may be prescribed low-dose testosterone, especially post-menopause, to boost mood, motivation, and bone strength as part of a holistic wellness approach.
Types of Testosterone Replacement: Gels, Injections, Patches, and More
Several delivery options exist for testosterone replacement therapy, each with pros and cons. Gels and creams offer a convenient, steady daily dose (rubbed into the skin); injections provide longer-lasting, more consistent blood levels (usually weekly); and patches deliver hormones through the skin with minimal fuss. Newer options, like subcutaneous pellets and oral medications, offer further choices. The best option balances effectiveness, safety, convenience, and individual preference—always under a healthcare provider's supervision and with routine lab monitoring for potential side effects.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Testosterone Therapy
- Prostate cancer risk considerations
- Cardiovascular effects
- Hormonal imbalances
"Testosterone therapy isn't a magic bullet—but for those with true deficiency, it can mean more energy, clearer thinking, and better quality of life." —Endocrinologist Dr. Carter
While testosterone replacement can offer benefits, it also carries side effects. In men, there is a potential increase in the risk of prostate cancer and cardiovascular events, so close medical supervision is a must. Others may develop acne, sleep apnea, or changes in cholesterol and blood pressure. For women, imbalanced dosing may cause unwanted hair growth or voice deepening. Continued research helps determine who stands to gain most with the fewest risks. Always approach hormone therapies thoughtfully and as part of a comprehensive, individualized plan.
Supporting Vitality: Natural Approaches to Healthy Testosterone and Aging
Lifestyle Habits to Boost Testosterone Without Medication
- Strength training and HIIT
- Adequate sleep
- Healthy fats in diet
- Stress management
- Avoiding environmental toxins
Supplements and Bioavailable Nutrients for Testosterone and Aging
The right supplements can gently support testosterone and aging without pharmaceutical side effects. Look for products with ingredients backed by clinical evidence, bioavailable forms your body can absorb, and natural, plant-based compounds whenever possible. Consider vitamin D, zinc, magnesium, D-aspartic acid, fenugreek, and ashwagandha—as well as specialized formulas in liquids, nano-drops, or quantum strips for faster, more complete absorption. Consult a knowledgeable healthcare provider for personalized recommendations before starting any new supplement regimen.
| Ingredient | Absorption Type | Clinical Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D3 | Lipid-soluble capsule/liquid | Strong support (RCTs show increased levels in deficiency) |
| Zinc | Tablet/liquid, picolinate form best | Moderate support, especially for those with low intake |
| Magnesium | Glycinate or citrate, nano-drops | Moderate support (aids free testosterone) |
| Ashwagandha | Capsule, extract | Emerging evidence; may boost male testosterone by reducing stress |
| D-Aspartic Acid | Powder, quantum strip | Supports short-term increase in certain men |
Products for Supporting Testosterone Production: Beware of Synthetic Claims
With the growing popularity of testosterone boosters, not all supplements are created the same. Some products use synthetic or untested ingredients that offer little real benefit—and may even suppress your body’s own production over time. Focus on science-backed, plant-based ingredients in bioavailable formats like liquids, nano-drops, and quantum strips for the greatest impact. These forms are absorbed faster and utilized more readily by the body, maximizing efficacy and supporting natural production for both men and women. Always check labels, look for third-party testing, and avoid products with “miracle cure” claims for safer, long-term results.
Testosterone and Aging: Key Takeaways for Lifelong Vitality
- Testosterone is vital for men and women
- Declines begin slowly but affect myriad aspects of health
- Balancing levels naturally supports long-term vitality
People Also Ask About Testosterone and Aging
Does testosterone make you age better?
Answer
Having healthy testosterone levels can help you maintain muscle mass, bone density, energy, and mental focus as you age. While it may not stop aging itself, balanced testosterone clearly supports many factors that help you stay stronger, sharper, and more resilient throughout life.
What are the side effects of taking testosterone?
Answer
Potential side effects of testosterone therapy include increased risk of prostate cancer in men, cardiovascular changes, acne, sleep disturbances, and, in women, changes to hair growth or voice. Only use testosterone treatments with a doctor’s guidance and appropriate monitoring.
What are the symptoms of low testosterone in men over 60?
Answer
For men over 60, symptoms of low testosterone include fatigue, reduced muscle mass, decreased bone density, mood changes, memory issues, and a reduced interest in sex. Early detection and lifestyle support can help prevent severe consequences like osteoporosis or frailty.
Is testosterone linked to aging?
Answer
Yes, testosterone is directly linked to the aging process. Its gradual decline contributes to many typical signs of aging—such as loss of strength, bone thinning, and shifts in motivation or mood—in both men and women. Addressing hormone health can support healthier aging.
Frequently Asked Questions about Testosterone and Aging
- How does testosterone decline affect women?
- What's a normal testosterone level at age 50?
- Can diet alone improve testosterone levels?
- Is testosterone therapy safe for everyone?
- Will exercise prevent testosterone loss as I age?
Conclusion: Enhancing Well-Being at Every Stage of Life
"Balanced testosterone is less about turning back the clock and more about making the most of every year—at any age."
With knowledge and smart daily choices, you can support balanced testosterone and enjoy lifelong strength, confidence, and vitality.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment