Did you know that starting as early as age 30, most men begin losing up to 1% of their testosterone each year? This isn’t just a number on a blood test—it means muscle mass may start to slip, daily energy might dip, and emotional balance can feel off. Yet, testosterone and muscle growth aren’t just about physical performance for bodybuilders or competitive athletes. They’re the pillars of physical vitality, mood, and lifelong resilience for everyone—men and women alike. If you want to maximize your health, harnessing the hidden power of testosterone could be your missing link.
Unveiling the Link: How Testosterone and Muscle Growth Shape Physical Vitality
“Testosterone isn’t just about performance — it’s about vitality, stability, and longevity for both men and women.”
- Startling Fact: By age 30, most men begin losing up to 1% of their testosterone levels per year, impacting muscle mass and emotional well-being.
- Testosterone and muscle growth: foundational for energy, recovery, and both physical and mental health.
- Implications for both men and women — not just athletes.

What You'll Learn about Testosterone and Muscle Growth
- The science behind testosterone levels and muscle mass
- Why both men and women need testosterone for strength and resilience
- How to support testosterone naturally and safely
- Understanding the risks of low testosterone and options for replacement therapy
The Science of Testosterone and Muscle Growth
Understanding Testosterone Level and Its Impact on Muscle Mass
- Differences between testosterone levels in men and women
- How testosterone influences muscle protein synthesis
- Role in muscle gain, metabolism, and bone strength
When it comes to building and maintaining muscle mass, testosterone is the body’s most powerful ally. Men generally have higher testosterone levels than women, which is why muscle gain usually occurs more rapidly for them. It’s not just a matter of size or strength—testosterone levels directly impact muscle protein synthesis, helping to repair and grow the muscle fibers stressed during training. In both men and women, optimal testosterone supports metabolism, improves the rate of muscle gain, and boosts bone strength—essential for injury prevention and longevity.
In contrast, low testosterone levels in men and women can lead to decreased muscle growth, increased fat accumulation, and a significant drop in both physical and emotional well-being. For older men and women approaching menopause, a dip in sex hormone production often brings noticeable changes in body mass and motivation. Understanding the physiological bridge between testosterone and muscle growth is key for anyone wanting to maintain or increase muscle mass, regardless of age or gender.
Protein Synthesis: Building Muscle with Optimal Testosterone
- The biological role of testosterone in muscle protein formation
- How muscle growth is stimulated by increased testosterone levels
Muscle protein synthesis is the body’s engine for repairing and building muscle tissue. Testosterone acts like a fuel additive here—raising levels of this hormone increases the efficiency of protein synthesis, accelerating muscle recovery and growth after weight training or resistance exercise. For anyone trying to build muscle (and keep muscle mass as they age), normal testosterone levels are essential for ongoing muscle health.
Research shows that even modest increases in testosterone, whether through training, nutrition, or targeted supplements, can produce big improvements in muscle gain and strength. This anabolic effect explains why athletes with naturally higher testosterone often outperform their peers—not only can they build muscle faster, but they also recover quicker and maintain better bone health. On the flip side, low level or declining testosterone decreases the body’s ability to synthesize muscle protein, undermining effort in the gym and daily life activities.
Testosterone Levels: Key Drivers of Muscle Mass and Strength
Factors Influencing Testosterone Level in Men and Women

- Age, lifestyle, and genetics
- Nutrition, sleep, stress, and exercise habits
Several crucial factors influence natural testosterone levels in both men and women. Genetics set your starting point, but lifestyle choices determine where your hormone levels go from there. As we age, testosterone level naturally falls, making it harder to maintain or build muscle—one reason many older men and women notice a loss of muscle, slower metabolism, and changes in mood. Nutrition plays a massive role, as diets low in essential fats, proteins, or select micronutrients can quickly lower testosterone. Chronic stress floods the body with cortisol, which suppresses testosterone production and interferes with muscle protein synthesis.
Quality sleep is another secret weapon; studies show that even one week of poor sleep can lead to lower testosterone levels and reduced muscle gain. Exercise, especially resistance and intense interval training, actively boosts the body’s production of this vital hormone, helping counteract the declines seen with aging or sedentary habits. Optimizing these daily lifestyle choices can be the most effective strategy for supporting healthy testosterone and muscle growth at any age.
Symptoms and Risks of Low Testosterone
- Warning signs: fatigue, low libido, loss of motivation
- Consequences for muscle mass, bone strength, and mental health
Low testosterone doesn’t just affect your ability to build muscle—it impacts your overall well-being. The early warning signs often include persistent fatigue, loss of sex drive, low motivation, and a general lack of energy. Over time, low testosterone levels can lead to a decrease in muscle mass, making it challenging to maintain or increase muscle even with regular training and adequate protein intake.
A decline in this essential hormone also damages bone strength, raising the risk of osteoporosis and fractures—especially in older men and women after menopause. Mental sharpness and emotional stability can suffer, too, with higher rates of depression reported in those experiencing hormone imbalances. If you notice several of these symptoms, consider consulting with a healthcare professional and requesting a blood test to assess your hormone status.
Why Testosterone Matters for Women’s Muscle Growth

- Unique hormone profile in women
- Importance for muscle tone, dopamine production, and metabolic health
It’s a persistent myth that testosterone is just a “male hormone.” In reality, women rely on it for many aspects of health, especially when it comes to muscle growth. Although women produce about one-tenth the testosterone of men, that smaller amount is critical for maintaining muscle tone, boosting metabolism, and feeling vibrant. When testosterone levels are optimal, women report not only greater physical strength but improved motivation and mental clarity, in part due to testosterone’s role in activating dopamine—your brain’s reward and resilience chemical.
After menopause, as testosterone levels dip lower, women often report increased body fat, loss of muscle, and declining mood. Supporting healthy testosterone production through lifestyle, nutrition, and supplementation keeps women strong, active, and emotionally balanced throughout life.
Build Muscle Naturally: Optimizing Testosterone for Maximum Gain
Exercise Strategies to Boost Testosterone and Muscle Growth
- Heavy resistance training and compound movements
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT)
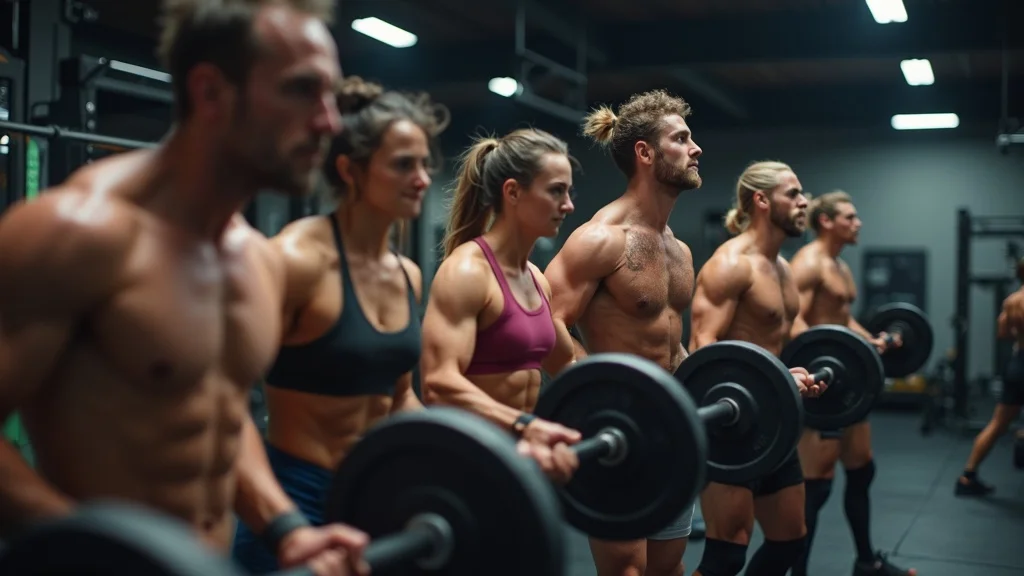

Want to build muscle and naturally maximize your testosterone level? Start with compound movements like squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and rows—a proven way to trigger both muscle gain and hormone boosts because they recruit large muscle groups and spike testosterone production. Integrating heavy resistance (lifting weights you can only manage for six to twelve reps) challenges your body, signaling a need to ramp up muscle protein synthesis.
Pair this approach with regular high-intensity interval training (HIIT). Quick, intense exercise spurts followed by short rest periods have been shown in multiple studies to temporarily increase testosterone production—perfect for both strength and cardiovascular health. Together, these methods create the best hormonal environment for muscle growth in both men and women, regardless of starting point or fitness history.
Dietary Tips to Support Testosterone Levels and Build Muscle Fast
- The role of healthy fats, protein, and micronutrients
- Foods to avoid for optimal hormone balance
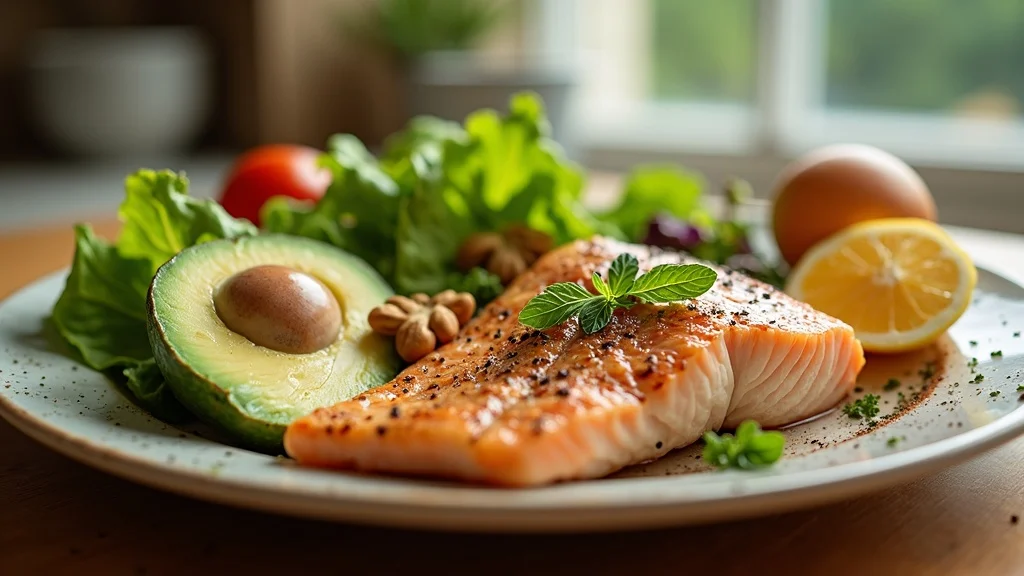

What you eat can make or break your efforts to support testosterone and muscle growth. Healthy fats (found in olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish) are essential for hormone synthesis—without enough dietary fat, the body can’t produce testosterone efficiently. High-quality protein is vital too, not just for muscle repair but for maximizing protein synthesis. Include sources such as eggs, lean meats, fish, and plant-based proteins with every meal.
Micronutrients like zinc, magnesium, and vitamin D also help sustain natural testosterone levels—oysters, pumpkin seeds, and leafy greens are among the top foods recommended by experts. Avoid excessive processed sugar, excessive alcohol, and highly processed foods, all of which can lower testosterone and inhibit muscle gain. Prioritizing a diet rich in whole foods and targeted nutrients empowers your body to optimize muscle gain and hormonal balance simultaneously.
Lifestyle Changes That Protect Testosterone and Enhance Muscle Gain
- The impact of sleep and stress management
- Avoiding endocrine disruptors that lower testosterone
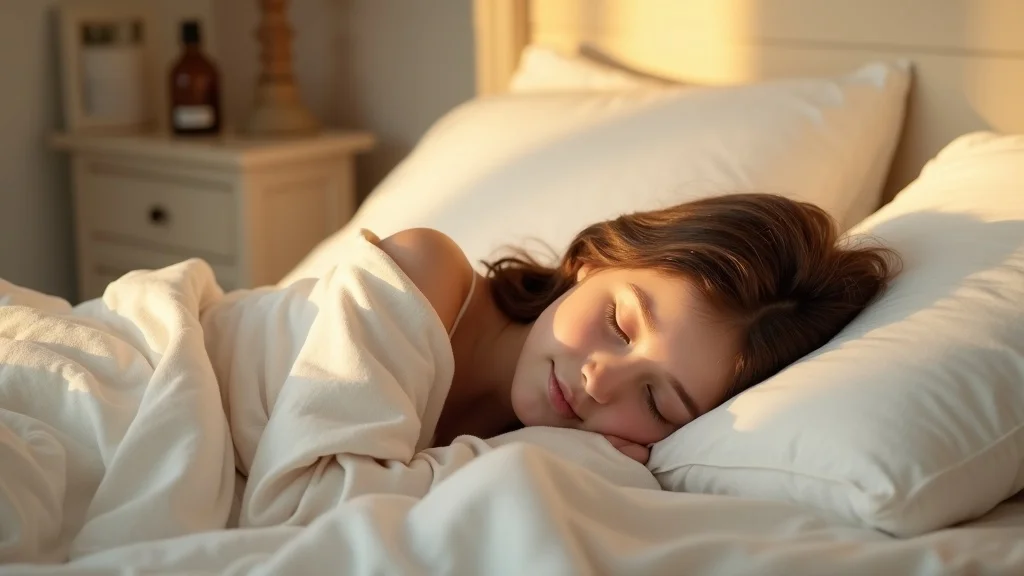

A holistic approach to testosterone levels and muscle growth must include regular, restorative sleep and mindful stress management. Aim for at least 7-9 hours of quality rest per night, as sleep is when the body produces the greatest amounts of growth and sex hormones. Chronic stress is a hidden testosterone killer—the more often your body is flooded with cortisol, the harder it becomes to maintain healthy hormone levels or build muscle.
Be vigilant about environmental endocrine disruptors too—chemicals in plastics, personal care products, and pesticides can lower testosterone production. Simple swaps for glass or stainless steel containers, natural grooming products, and organic food make a significant difference. Small, consistent adjustments in sleep, stress modulation, and toxin avoidance can yield big improvements in muscle mass and hormone health overall.
| Nutrient | Best Food Sources | Role in Muscle/Testosterone Health |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc | Oysters, pumpkin seeds, beef, lentils | Boosts natural testosterone production |
| Vitamin D | Salmon, eggs, fortified dairy, sunlight | Regulates testosterone levels, supports muscle function |
| Healthy Fats | Olive oil, fatty fish, nuts, avocado | Essential for hormone synthesis and muscle gain |
| Protein | Chicken, eggs, plant proteins, Greek yogurt | Provides amino acids for muscle protein synthesis |
| Magnesium | Spinach, almonds, black beans, dark chocolate | Supports testosterone bioavailability |
Testosterone Replacement Therapy: When Is It Necessary for Muscle Mass?
Indications for Testosterone Replacement Therapy
- Diagnosing low testosterone: testing and thresholds
- Who qualifies for replacement therapy
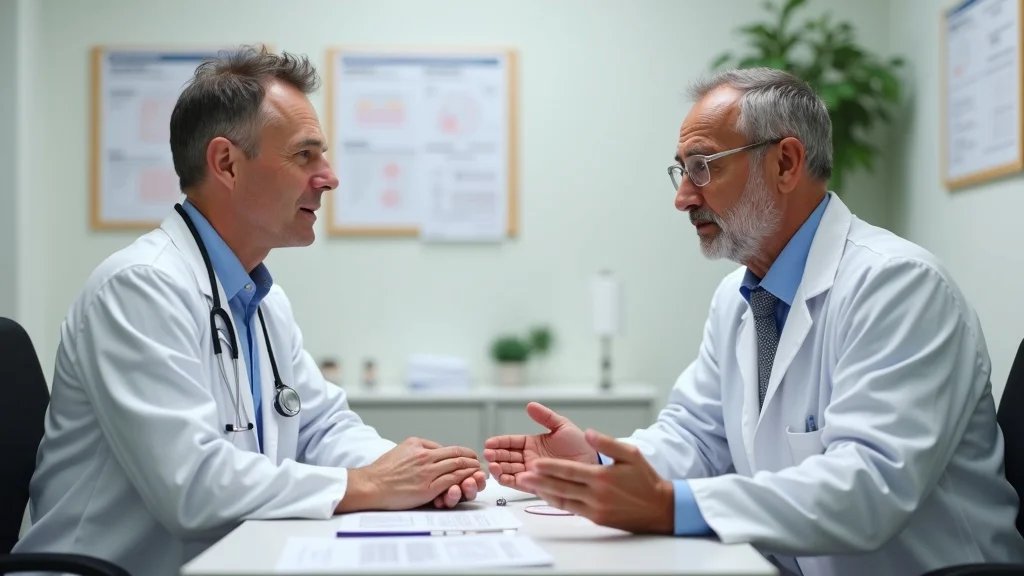

While most people can support testosterone naturally, some require testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) due to medical conditions that cause very low levels of testosterone. This is usually determined via a comprehensive blood test and symptom assessment. Candidates for replacement therapy are those with clear clinical signs—persistent fatigue, loss of muscle mass, low libido, and other symptoms—supported by documented low testosterone confirmed by laboratory tests.
It’s crucial to undergo proper diagnosis, since replacement therapy isn’t necessary or safe for everyone. Factors such as other medical conditions, current medication use, and age also influence whether therapy is recommended. For some, addressing lifestyle factors may be the first—and sometimes only—step needed to restore normal testosterone levels and gain back muscle mass.
Potential Benefits and Risks of Testosterone Replacement
- Quick muscle gain: the reality
- Side effects and long-term considerations
The promise of quick muscle gain is one reason some seek out testosterone replacement therapy, but the decision isn’t straightforward. While TRT can help restore muscle protein synthesis and energy in those with genuinely low testosterone, it may be accompanied by unwanted side effects—including fluid retention, acne, mood swings, and sleep apnea. Longer-term risks such as cardiovascular complications and an increased chance of prostate health problems have also been reported, especially in older men or when used without medical oversight.
Monitoring and moderation are key—too much testosterone, especially from synthetic or unregulated sources, can disrupt your body’s own hormone balance and lead to serious health complications. Clinical supervision ensures that testosterone replacement is used only when truly indicated, helping you achieve stable muscle growth without sacrificing safety.
Natural Alternatives to Testosterone Replacement
- Plant-based nutrients and effective supplementation
- How to support muscle growth and testosterone naturally

For most, the best way to optimize testosterone and muscle growth is through a targeted natural approach. Several plant-based nutrients—such as fenugreek, ashwagandha, and ginseng—have been clinically shown to bolster natural testosterone production, supporting muscle gain without the side effects of synthetic hormone therapy. Adaptogens, healthy fats, protein-rich foods, and micronutrients all contribute to healthy hormone production and the capacity to build muscle efficiently.
Focus on a holistic plan: regular strength training, adequate restorative sleep, stress management, and eliminating environmental toxins work together to amplify your results. When combined with smart supplementation, most people can achieve impressive gains in both muscle mass and overall energy, bypassing the risks of replacement therapy.
“Supporting your body’s own testosterone production, with the right nutrients and lifestyle, is often safer and more sustainable than synthetic hormone therapy.” — Endocrinology Expert
Common Questions About Testosterone and Muscle Growth
Does testosterone improve muscle growth?
- Testosterone regulates muscle protein synthesis, directly impacting muscle gain
- Both natural and clinical evidence support its role in maximizing muscle growth
Yes, testosterone directly improves muscle growth by ramping up the process of muscle protein synthesis. Multiple studies confirm that people with higher testosterone levels build muscle more efficiently and recover faster. Athletic performance, increased body mass, and greater strength are all closely tied to optimal testosterone, regardless of sex.
Can testosterone cause headaches?
- Possible side effect, especially with synthetic or excessive supplementation
- Monitoring and moderation for safety
Yes, headaches can be a side effect of testosterone supplementation—especially if dosage is too high or not clinically supervised. Adjustments to dosage and ensuring medical oversight reduce the risk. If you experience frequent headaches during therapy, notify your provider promptly.

Will 200mg of testosterone a week build muscle?
- Clinical overview: dosage, effectiveness, and health implications
- Dangers of unsupervised use
A weekly dose of 200mg testosterone is clinical-strength and may lead to rapid muscle gain—but only when prescribed for medical reasons and monitored through blood tests. Using this amount without supervision may cause serious health risks, including hormonal disruption and other adverse side effects.
Can I build muscle with low testosterone?
- Challenges and strategies for individuals with low testosterone
- Alternatives and lifestyle adjustments for muscle gain
It is possible to build muscle with low testosterone, but the process is slower and requires extra effort in terms of training, nutrition, sleep, and stress reduction. Focusing on these natural levers, along with targeted supplementation, can help maximize your body’s ability to gain and maintain muscle—safely and sustainably. Verification by a healthcare provider is recommended if you struggle with chronic muscle loss and other symptoms of low testosterone.
Quick Reference: Answers to Frequently Asked Questions
- Can women benefit from testosterone for muscle growth?
- How long does it take to see muscle gain?
- What are the common symptoms of low testosterone?
- Is testosterone replacement therapy safe?
- Are there natural boosters that really work?
- Yes, it supports muscle tone and overall well-being in women.
- Noticeable gains can appear within weeks to months with optimal testosterone.
- Fatigue, low mood, loss of muscle and libido — see your doctor if you notice persistent changes.
- It requires medical supervision due to risks and side effects.
- Certain botanicals and lifestyle shifts are clinically shown to help.

Key Takeaways: Testosterone and Muscle Growth Essentials
- Testosterone and muscle growth are interlinked — supporting one supports the other.
- Both men and women need healthy testosterone levels for optimal strength, mood, and longevity.
- Lifestyle, nutrition, and targeted supplements can naturally maximize both testosterone and muscle gain.
- Seek professional advice before considering replacement therapy.
Conclusion: Empowering Muscle Growth Through Healthy Testosterone
- Testosterone laid the foundation for your energy, recovery, and confidence.
- Balanced hormone levels can transform how you look, feel, and perform.
“Great muscle health starts with understanding — and supporting — the hormones that build it. Healthy muscle, healthy life.”

Discover Supplements for Testosterone and Muscle Growth
- 💧 Want to feel the difference absorption makes? See the supplements we recommend for maximum impact — and why liquids, nano-drops, and quantum strips work better.👉 Discover Our Top Picks →
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment